Aquarium fish diseases can be a major concern for fish owners. Healthy fish require proper care and attention to avoid illnesses.
Fish, like any pets, can get sick. Knowing common diseases helps in prevention and treatment. Understanding fish health is crucial for maintaining a thriving aquarium. Fish diseases can spread quickly and affect all tank inhabitants. Early detection and treatment are key to saving your fish.
Many diseases result from poor water quality, stress, or infections. By recognizing symptoms early, you can take action to improve your fish’s health. In this blog, we will explore common aquarium fish diseases. Learn how to identify, prevent, and treat these issues to keep your aquarium vibrant and healthy. Stay informed and give your fish the care they deserve.
Common Fish Diseases
Fish diseases can turn your beautiful aquarium into a stressful place. Knowing common fish diseases helps you keep your fish healthy. Here are some of the most common fish diseases you should be aware of.
Ich
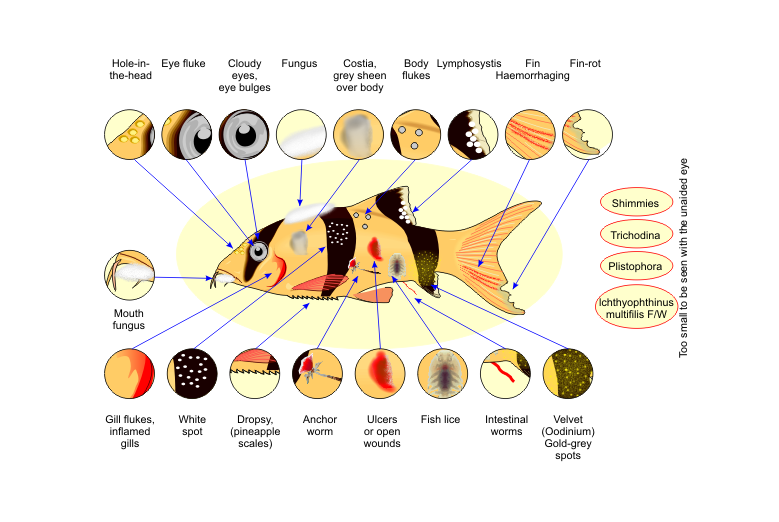
Ich, also known as white spot disease, is very common in aquarium fish. It appears as white spots on the skin, gills, and fins of the fish. The parasite responsible for this disease is called Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Fish with Ich may scrape against objects in the tank due to irritation. Immediate treatment is crucial to prevent the spread.
Fin Rot
Fin Rot is another prevalent disease. It causes the edges of the fins to become ragged and discolored. Bacteria usually cause fin rot, but poor water conditions can make it worse. Fish suffering from fin rot may also show signs of lethargy. Clean water and proper medication can help treat this condition.
Swim Bladder Disease
Swim Bladder Disease affects a fish’s buoyancy. Fish with this disease may float to the top or sink to the bottom of the tank. Overfeeding or infections can cause swim bladder issues. Symptoms include difficulty swimming and an abnormal position in the water. Feeding the fish peas can sometimes help, as it aids digestion.
| Common Fish Diseases | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ich | Parasites | White spots, scratching against objects | Medication, clean water |
| Fin Rot | Bacteria | Ragged fins, lethargy | Clean water, antibiotics |
| Swim Bladder Disease | Overfeeding, infection | Difficulty swimming, abnormal position | Feeding peas, reducing food |
Keeping a close eye on your fish is key to early detection. Regular water changes and a balanced diet can prevent many issues. Ensure you quarantine new fish to avoid introducing diseases to your tank.
Symptoms To Watch For
Keeping your aquarium fish healthy is crucial. Recognizing early symptoms of diseases can save your fish. Below are key signs to watch for.
Behavioral Changes
Unusual behavior is a red flag. Healthy fish are active and alert. Look for these changes:
- Fish staying at the surface or bottom.
- Loss of appetite.
- Erratic swimming patterns.
- Rubbing against objects.
Physical Signs
Physical signs are easier to spot. Regularly inspect your fish. Key physical symptoms include:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| White Spots | Indicates Ich disease. |
| Red Streaks | Possible bacterial infection. |
| Bloated Body | May indicate dropsy. |
| Clamped Fins | Sign of stress or illness. |
Color Changes
Color changes can indicate health problems. Healthy fish have vibrant colors. Watch for:
- Faded colors.
- Darkening of the skin.
- Unusual spots or patches.
Being vigilant about these symptoms helps maintain a healthy aquarium environment.
Preventive Measures
Keeping your aquarium fish healthy is essential. Preventive measures can save you from dealing with diseases. A healthy environment and regular care are key. The following sections will guide you on how to prevent common fish diseases.
Quarantine New Fish
Always quarantine new fish before adding them to your main tank. This prevents the spread of potential diseases. A quarantine tank should be separate and well-maintained.
- Keep new fish in quarantine for at least two weeks.
- Observe them for signs of illness.
- Treat any visible disease before moving them.
Regular Water Changes
Changing the water regularly keeps the environment clean. Dirty water can cause stress and illness in fish. Follow a simple schedule for water changes.
- Replace 10-20% of the water weekly.
- Use a water conditioner to remove chlorine.
- Check and maintain the right pH levels.
Proper Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for fish health. Different species have different dietary needs. Ensure you feed them the right food.
| Fish Type | Diet |
|---|---|
| Herbivores | Vegetables, algae wafers |
| Carnivores | Live or frozen food, pellets |
| Omnivores | A mix of vegetables and protein |
Feed your fish small amounts. Overfeeding can lead to waste buildup and water pollution.
Credit: www.bunnycart.com
Treatment Options
Aquarium fish diseases can be challenging, but effective treatments exist. Understanding the various treatment options can help you keep your fish healthy. Below, we explore some common methods to treat fish diseases.
Medications
Medications are often the first line of defense against fish diseases. They come in various forms, such as:
- Antibiotics – Used for bacterial infections.
- Antifungals – Treat fungal infections.
- Antiparasitics – Combat parasitic infestations.
Follow the instructions on the medication package carefully. Overdosing can harm your fish. Always quarantine sick fish to avoid spreading the disease.
Salt Baths
Salt baths can be an effective treatment for many fish diseases. They help remove parasites and heal wounds. Here’s how to perform a salt bath:
- Prepare a separate tank with dechlorinated water.
- Add non-iodized salt at a ratio of 1 tablespoon per gallon.
- Place the sick fish in the salt bath for 5-10 minutes.
- Monitor the fish closely for stress signs.
- Return the fish to its regular tank.
Repeat the process daily until the fish shows improvement. Use salt baths with caution, as some fish species are sensitive to salt.
Temperature Adjustment
Adjusting the water temperature can help treat certain fish diseases. Higher temperatures can speed up the life cycle of parasites, making them easier to eliminate. Follow these steps:
- Gradually increase the water temperature by 1-2°F per day.
- Do not exceed the maximum safe temperature for your fish species.
- Maintain the higher temperature for several days.
- Gradually lower the temperature back to normal.
Always monitor your fish for signs of stress during temperature adjustments.
Importance Of Water Quality
Maintaining excellent water quality is crucial for the health of your aquarium fish. Poor water conditions can lead to stress and disease. Ensuring the water is clean and balanced helps prevent many common fish diseases. Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential tasks for any aquarium owner.
Ph Levels
The pH level of your aquarium water plays a vital role in fish health. Most freshwater fish thrive in a pH range of 6.5 to 7.5. Sudden changes in pH can stress fish, making them more susceptible to diseases. Regularly test the pH levels using a reliable test kit. Adjust the pH gradually if needed to avoid shocking the fish.
Ammonia And Nitrite
Ammonia and nitrite are toxic to fish. These compounds result from fish waste and uneaten food. High levels can cause severe health issues and even death. Monitor these levels closely using test kits. Keep ammonia and nitrite levels as close to zero as possible. Perform regular water changes and ensure proper filtration to control these toxins.
Filtration Systems
A good filtration system is essential for maintaining water quality. Filters help remove debris, excess food, and waste products. There are three main types of filtration:
- Mechanical Filtration: Removes solid particles from the water.
- Biological Filtration: Uses beneficial bacteria to break down toxic substances.
- Chemical Filtration: Removes dissolved contaminants using activated carbon or other chemicals.
Ensure your filter is appropriately sized for your aquarium. Clean and maintain the filter regularly to keep it functioning effectively. A well-maintained filter can significantly reduce the risk of fish diseases.
Role Of Nutrition
Proper nutrition is crucial for the health of aquarium fish. A well-balanced diet helps prevent diseases and promotes a strong immune system. Let’s explore the role of nutrition in keeping your fish healthy.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet includes a mix of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Different fish species have specific dietary needs. For instance:
- Herbivores: Need plant-based foods.
- Carnivores: Require protein-rich foods.
- Omnivores: Thrive on a mix of both.
Feeding a variety of foods ensures your fish get all essential nutrients. Consider including:
- Flake food
- Pellets
- Frozen or live foods
Supplements
Supplements can enhance your fish’s diet. They provide extra vitamins and minerals. Common supplements include:
- Vitamin C: Boosts immunity.
- Calcium: Strengthens bones.
- Spirulina: Enhances color and vitality.
Always follow the recommended dosage to avoid over-supplementation.
Feeding Schedule
Establishing a consistent feeding schedule is essential. Overfeeding can lead to health problems and water pollution. Here are some tips:
- Feed small amounts 2-3 times a day.
- Remove uneaten food after 5 minutes.
- Observe your fish to adjust feeding amounts.
Consistency helps maintain your fish’s health and water quality.
Quarantine Tanks
Quarantine tanks are vital for maintaining the health of your aquarium fish. These tanks help prevent the spread of diseases by isolating new or sick fish. Using a quarantine tank can save your entire aquarium from potential outbreaks.
Setting Up
Setting up a quarantine tank is simple but requires attention to detail. Start with a separate tank, ideally 10-20 gallons, depending on your fish size. Make sure to use a heater and filter to maintain water quality. Add a thermometer to monitor temperature and a sponge filter for biological filtration.
Use a bare-bottom tank to make cleaning easier. Add a few hiding spots like PVC pipes or small decorations for the fish to feel safe. Do not use substrate or plants, as they can harbor pathogens.
Maintenance
Maintaining a quarantine tank requires regular care. Perform daily water changes of 10-20% to keep the water clean. Monitor the water parameters closely, including ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels.
Feed the fish sparingly to reduce waste. Remove uneaten food promptly to prevent water contamination. Use a separate set of tools for the quarantine tank to avoid cross-contamination with your main tank.
Duration
The duration of quarantine depends on the fish’s health. Generally, new fish should stay in quarantine for at least 2-4 weeks. Observe them for signs of disease, such as white spots, fin rot, or lethargy.
If you notice any symptoms, extend the quarantine period and start treatment immediately. Only transfer the fish to the main tank when they show no signs of illness for at least a week.
Quarantine tanks are an essential part of fishkeeping. They protect your main aquarium from diseases and ensure your fish stay healthy.

Credit: greenaqua.hu
When To Consult A Veterinarian
Fish diseases can be tricky to diagnose and treat. Knowing when to consult a veterinarian is crucial for the health of your aquarium fish. Sometimes, home remedies are not enough. Professional help ensures your fish receive the best care.
Persistent Symptoms
Persistent symptoms indicate serious issues. If your fish show signs like constant lethargy, loss of appetite, or abnormal swimming, it’s time to seek help. Symptoms lasting more than a week are concerning.
Other symptoms to watch for include:
- White spots or patches on the body
- Red or swollen gills
- Rapid breathing
These could signal infections or parasites that need specialist care.
Specialist Treatment
Some conditions require specialist treatment. Vets can diagnose complex issues like bacterial infections or internal parasites. They use advanced tools and tests that are not available to hobbyists.
Specialist treatments may include:
- Antibiotic injections
- Surgery for removing tumors
- Prescription medications
Early diagnosis and treatment improve the chances of recovery.
Emergency Situations
Emergency situations need immediate attention. If your fish are gasping for air at the surface or lying on the tank bottom, call a vet right away. Quick action can save their lives.
Other emergencies include:
- Severe injuries or bleeding
- Sudden bloating or swelling
- Massive outbreaks of disease
Don’t wait if you notice these signs. Emergency care is vital.

Credit: aquariumstoredepot.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common Aquarium Fish Diseases?
Common aquarium fish diseases include Ich, fin rot, and swim bladder disease. Regular monitoring and maintaining water quality can help prevent these issues.
How Do I Treat Ich In Fish?
To treat Ich, raise the water temperature gradually and use a commercial Ich treatment. Quarantine affected fish to prevent spreading.
Why Do Fish Get Fin Rot?
Fish get fin rot from poor water quality, stress, or injuries. Improve water conditions and use antibacterial treatments to help recovery.
How Can I Prevent Fish Diseases?
Prevent fish diseases by maintaining clean water, not overfeeding, and quarantining new fish before adding them to the aquarium.
Conclusion
Healthy fish bring joy to any aquarium. Regularly check for signs of disease. Quick action prevents many problems. Consult a vet if unsure about symptoms. Clean water helps fish stay healthy. Feed them a balanced diet. Observe fish behavior daily.
Happy fish mean a happy tank. Keep learning about fish care. Your fish will thank you!



